Download operating system
for your personal computer.
Fedora Linux 39 (November, 2023) Workstation 64-bit Official ISO Disk Image Download
Description
Fedora Linux 39 was released in November, 2023, preceded by version 38, and was designed for desktop / laptop computers, and servers. Only the 64-bit version is available for Fedora Linux 39. Compared to the previous Fedora release, this version includes some new updates, such as GNOME 45, which offers improved performance and usability improvements, including a new workspace switcher and image viewer. The release also includes Fedora Onyx, a Budgie-based desktop, as well as updates to other desktop flavors like KDE Plasma desktop, XFCE, Cinnamon, and others. Additionally, Fedora cloud images are now available in Microsoft Azure, and cloud images are configured for optional auto-update and provisioning upon reboot. The release brings package updates including GCC 13.2, binutils 2.40, glibc 2.38, gdb 13.2, rpm 4.19, Python 3.12, and Rust 1.73. The vector graphics tool Inkscape has also been updated in this release.
For more information, read the release document of Fedora Linux 39.
From version 31 onwards, Fedora dropped support for the 32-bit platform.
General information from Fedora
Fedora is a free and open source Linux operating system (or distribution) that has been developed by contributions from community members and Red Hat. Fedora was designed for personal computers and servers, and is currently available in three different editions, which are for Workstation (for personal computer), Server (for servers), and Atomic (for cloud computing). GNOME is currently the default desktop environment for the operating system, and the GNOME Shell is the default user interface. There are more other desktop environments supported in Fedora, such as Cinnamon, Xfce, and MATE. Like other Linux distributions, Fedora is bundled with many general software applications such as Firefox Browser, LibreOffice, Media Player etc.
Specification
| Available in | 35+ languages |
| CPU Platform(s) | X86-64 |
| License | Free and open-source software |
System requirements
Minimum:
- 2GHz dual-core processor or faster.
- 15 GB of hard disk space.
- 2 GB of RAM.
Installation Instructions
Follow the steps given below:
- Download the Fedora Linux 39 ISO image file from the download section.
- Install a USB bootable creation software on your Windows PC.
- Plug in a USB flash drive (at least 4 GB of free space available) with your PC.
- Open the USB bootable creation software, and select the ISO image file of Fedora Linux 39, and start the process.
- As soon as done, plug the bootable USB into a system where you want to install Fedora Linux 39.
- Restart the target computer.
- Press the boot device menu key and select USB to boot first.
- Select USB device and start the Fedora Linux 39 installer.
Starting installer in VMware
- Download the Fedora Linux 39 ISO image file from the download section.
- Launch the VMware Player, and start creating a new virtual machine.
- Select the ISO image file of Fedora Linux 39, and use the default settings for the virtual machine.
- Start the virtual machine and go to the Fedora Linux 39 installer.
Starting installer in VirtualBox
- Download the Fedora Linux 39 ISO image file from the download section.
- Launch the Virtualbox application on your computer, and start creating a new virtual machine.
- Select Ubuntu and use defualt settings for the virtual machine.
- Start VM and when it asks to select the Host Drive, then select the downloaded Fedora Linux 39 ISO file in step 1.
Last step
As soon as you go to the Fedora Welcome Screen, follow the steps given below:
- Proceed on the welcome screen.
- Accept the license agreement, and proceed.
- Configure firewall, date / time, etc.
- Create root user.
- Follow on-screen instructions, and complete the installation.
- Log in to Fedora using your username and password.
- Do not forget to remove the installation medium from the computer (for example, USB, CD / DVD).
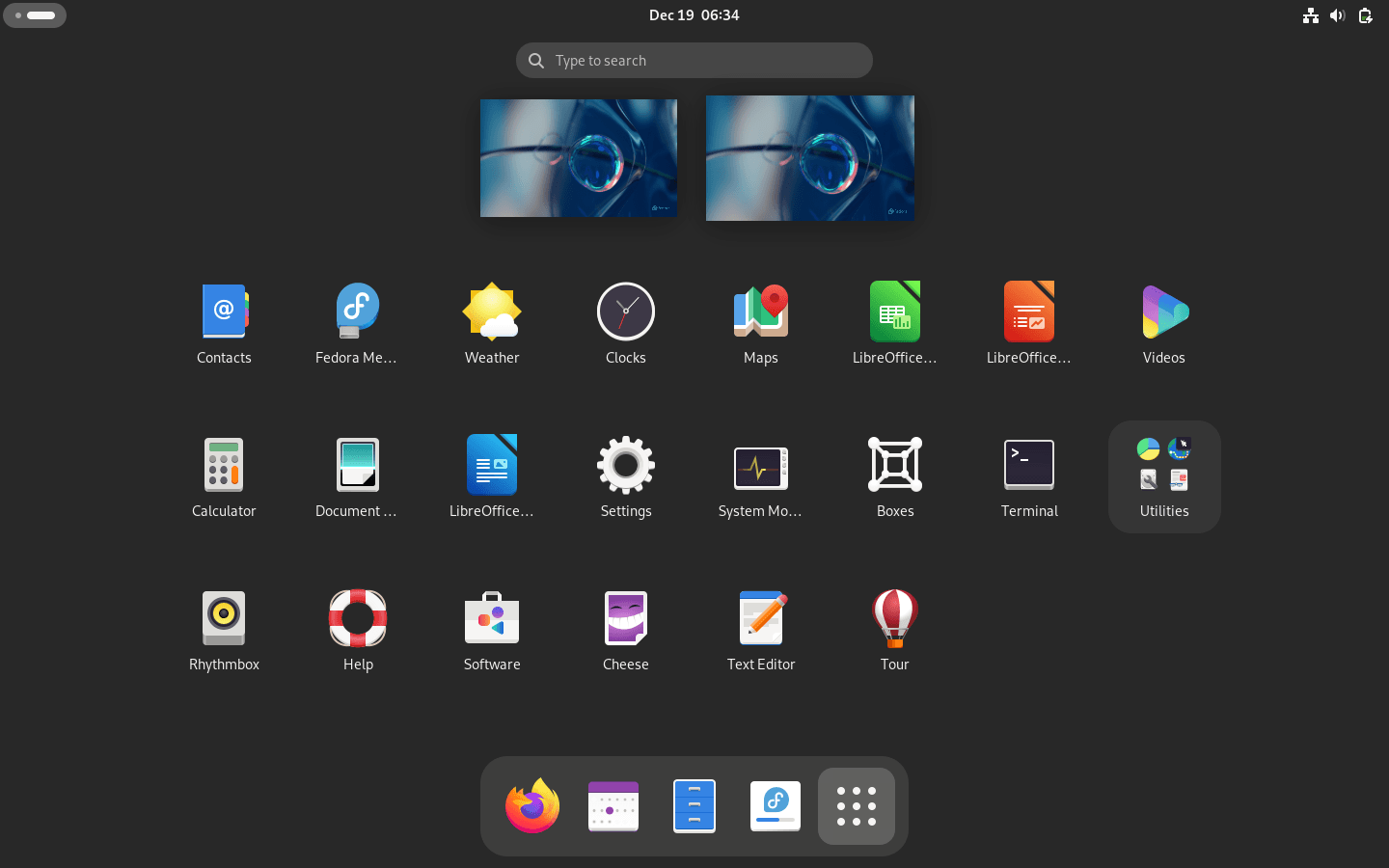
Screenshots